# Weights and Biases
Use W&B to build better models faster. Track and visualize all the pieces of your machine learning pipeline, from datasets to production models.
- Quickly identify model regressions. Use W&B to visualize results in real time, all in a central dashboard.
- Focus on the interesting ML. Spend less time manually tracking results in spreadsheets and text files.
- Capture dataset versions with W&B Artifacts to identify how changing data affects your resulting models.
- Reproduce any model, with saved code, hyperparameters, launch commands, input data, and resulting model weights.
[Sign up for a free account →](https://wandb.com)
需要注册登录,生成token,才能可视化。。。
Install `wandb` library and login:
```
pip install wandb
wandb login
```
Flexible integration for any Python script:
```python
import wandb
# 1. Start a W&B run
wandb.init(project="gpt3")
# 2. Save model inputs and hyperparameters
config = wandb.config
config.learning_rate = 0.01
# Model training code here ...
# 3. Log metrics over time to visualize performance
for i in range(10):
wandb.log({"loss": loss})
```
### [Try in a colab →](http://wandb.me/intro)
If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to ask in our [user forum](http://wandb.me/forum).

**[Explore a W&B dashboard](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gnD8BFuyVUA)**
# Academic Researchers
If you'd like a free academic account for your research group, [reach out to us →](https://www.wandb.com/academic)
We make it easy to cite W&B in your published paper. [Learn more →](https://www.wandb.com/academic)
[](https://www.wandb.com/academic)
# 📈 Track model and data pipeline hyperparameters
Set `wandb.config` once at the beginning of your script to save your hyperparameters, input settings (like dataset name or model type), and any other independent variables for your experiments. This is useful for analyzing your experiments and reproducing your work in the future. Setting configs also allows you to [visualize](https://docs.wandb.com/sweeps/visualize-sweep-results) the relationships between features of your model architecture or data pipeline and the model performance (as seen in the screenshot above).
```python
wandb.init()
wandb.config.epochs = 4
wandb.config.batch_size = 32
wandb.config.learning_rate = 0.001
wandb.config.architecture = "resnet"
```
- **[See how to set configs in a colab →](http://wandb.me/config-colab)**
- [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/library/config)
# 🏗 Use your favorite framework
## 🥕 Keras
In Keras, you can use our callback to automatically save all the metrics tracked in `model.fit`. To get you started here's a minimal example:
```python
# Import W&B
import wandb
from wandb.keras import WandbCallback
# Step1: Initialize W&B run
wandb.init(project="project_name")
# 2. Save model inputs and hyperparameters
config = wandb.config
config.learning_rate = 0.01
# Model training code here ...
# Step 3: Add WandbCallback
model.fit(
X_train, y_train, validation_data=(X_test, y_test), callbacks=[WandbCallback()]
)
```
- **[Try in a colab →](http://wandb.me/keras-colab)**
- [Learn More](https://app.wandb.ai/wandb/getting-started/reports/Keras--VmlldzoyMTEwNjQ)
- [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/library/integrations/keras)
## 🔥 PyTorch
W&B provides first class support for PyTorch. To automatically log gradients and store the network topology, you can call `.watch` and pass in your PyTorch model.
Then use `.log` for anything else you want to track, like so:
```python
import wandb
# 1. Start a new run
wandb.init(project="gpt-3")
# 2. Save model inputs and hyperparameters
config = wandb.config
config.dropout = 0.01
# 3. Log gradients and model parameters
wandb.watch(model)
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
...
if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
# 4. Log metrics to visualize performance
wandb.log({"loss": loss})
```
- **[Try in a colab →](http://wandb.me/pytorch-colab)**
- [Learn More](https://app.wandb.ai/wandb/getting-started/reports/Pytorch--VmlldzoyMTEwNzM)
- [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/library/integrations/pytorch)
## 🌊 TensorFlow
The simplest way to log metrics in TensorFlow is by logging `tf.summary` with our TensorFlow logger:
```python
import wandb
# 1. Start a W&B run
wandb.init(project="gpt3")
# 2. Save model inputs and hyperparameters
config = wandb.config
config.learning_rate = 0.01
# Model training here
# 3. Log metrics over time to visualize performance
with tf.Session() as sess:
# ...
wandb.tensorflow.log(tf.summary.merge_all())
```
- **[Try in a colab →](http://wandb.me/tf-colab)**
- [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/library/integrations/tensorflow)
## 💨 fastai
Visualize, compare, and iterate on fastai models using Weights & Biases with the `WandbCallback`.
```python
import wandb
from fastai.callback.wandb import WandbCallback
# 1. Start a new run
wandb.init(project="gpt-3")
# 2. Automatically log model metrics
learn.fit(..., cbs=WandbCallback())
```
- **[Try in a colab →](http://wandb.me/fastai-colab)**
- [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/library/integrations/fastai)
## ⚡️ PyTorch Lightning
Build scalable, structured, high-performance PyTorch models with Lightning and log them with W&B.
```python
from pytorch_lightning.loggers import WandbLogger
from pytorch_lightning import Trainer
wandb_logger = WandbLogger(project="gpt-3")
trainer = Trainer(logger=wandb_logger)
```
- **[Try in a colab →](http://wandb.me/lightning)**
- [Docs](https://docs.wandb.ai/guides/integrations/lightning)
## 🤗 HuggingFace
Just run a script using HuggingFace's Trainer passing `--report_to wandb` to it
in an environment where `wandb` is installed, and we'll automatically log losses,
evaluation metrics, model topology, and gradients:
```shell
# 1. Install the wandb library
pip install wandb
# 2. Run a script that has the Trainer to automatically logs metrics, model topology and gradients
python run_glue.py \
--report_to wandb \
--model_name_or_path bert-base-uncased \
--task_name MRPC \
--data_dir $GLUE_DIR/$TASK_NAME \
--do_train \
--evaluate_during_training \
--max_seq_length 128 \
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 32 \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 3 \
--output_dir /tmp/$TASK_NAME/ \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--logging_steps 50
```
- **[Try in a colab →](http://wandb.me/hf)**
- [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/library/integrations/huggingface)
# 🧹 Optimize hyperparameters with Sweeps
Use Weights & Biases Sweeps to automate hyperparameter optimization and explore the space of possible models.
### [Get started in 5 mins →](https://docs.wandb.com/sweeps/quickstart)
### [Try Sweeps in PyTorch in a Colab →](http://wandb.me/sweeps-colab)
### Benefits of using W&B Sweeps
- **Quick to set up:** With just a few lines of code you can run W&B sweeps.
- **Transparent:** We cite all the algorithms we're using, and our code is [open source](https://github.com/wandb/sweeps).
- **Powerful:** Our sweeps are completely customizable and configurable. You can launch a sweep across dozens of machines, and it's just as easy as starting a sweep on your laptop.
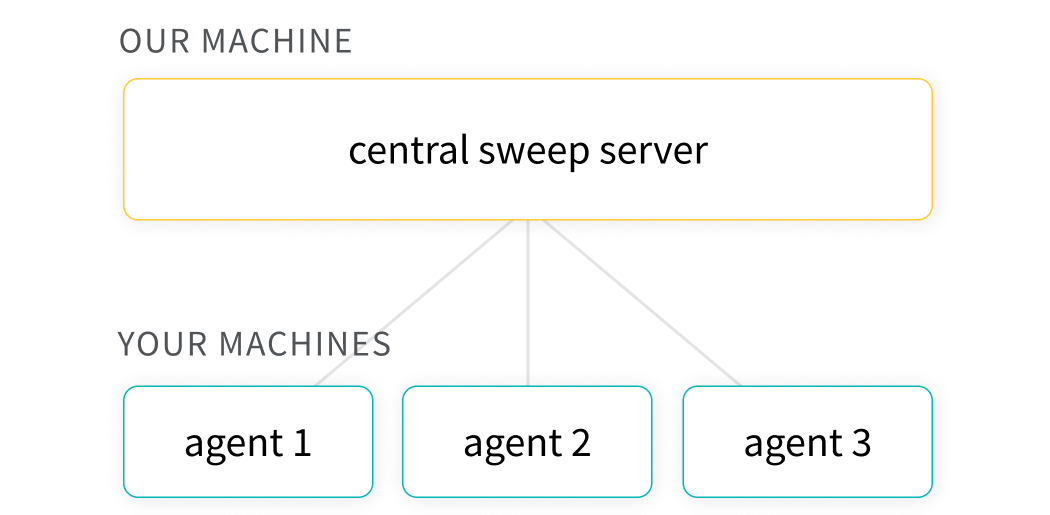 ### Common use cases
- **Explore:** Efficiently sample the space of hyperparameter combinations to discover promising regions and build an intuition about your model.
- **Optimize:** Use sweeps to find a set of hyperparameters with optimal performance.
- **K-fold cross validation:** [Here's a brief code example](https://github.com/wandb/examples/tree/master/examples/wandb-sweeps/sweeps-cross-validation) of _k_-fold cross validation with W&B Sweeps.
### Visualize Sweeps results
The hyperparameter importance plot surfaces which hyperparameters were the best predictors of, and highly correlated to desirable values for your metrics.
### Common use cases
- **Explore:** Efficiently sample the space of hyperparameter combinations to discover promising regions and build an intuition about your model.
- **Optimize:** Use sweeps to find a set of hyperparameters with optimal performance.
- **K-fold cross validation:** [Here's a brief code example](https://github.com/wandb/examples/tree/master/examples/wandb-sweeps/sweeps-cross-validation) of _k_-fold cross validation with W&B Sweeps.
### Visualize Sweeps results
The hyperparameter importance plot surfaces which hyperparameters were the best predictors of, and highly correlated to desirable values for your metrics.
 Parallel coordinates plots map hyperparameter values to model metrics. They're useful for honing in on combinations of hyperparameters that led to the best model performance.
Parallel coordinates plots map hyperparameter values to model metrics. They're useful for honing in on combinations of hyperparameters that led to the best model performance.
 # 📜 Share insights with Reports
Reports let you [organize visualizations, describe your findings, and share updates with collaborators](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o2dOSIDDr1w&&ab_channel=Weights%26Biases).
### Common use cases
- **Notes:** Add a graph with a quick note to yourself.
- **Collaboration:** Share findings with your colleagues.
- **Work log:** Track what you've tried and plan next steps.
**Explore reports in [The Gallery →](https://app.wandb.ai/gallery) | Read the [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/reports)**
Once you have experiments in W&B, you can visualize and document results in Reports with just a few clicks. Here's a quick [demo video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jWBGKGAjt6w&t=2s&ab_channel=Weights%26Biases).

# 🏺 Version control datasets and models with Artifacts
Git and GitHub make code version control easy,
but they're not optimized for tracking the other parts of the ML pipeline:
datasets, models, and other large binary files.
W&B's Artifacts are.
With just a few extra lines of code,
you can start tracking you and your team's outputs,
all directly linked to run.
### [Try Artifacts in a Colab →](http://wandb.me/artifacts-colab)

### Common use cases
- **Pipeline Management:** Track and visualize the inputs and outputs of your runs as a graph
- **Don't Repeat Yourself™:** Prevent the duplication of compute effort
- **Sharing Data in Teams:** Collaborate on models and datasets without all the headaches

**Learn about Artifacts [here →](https://www.wandb.com/articles/announcing-artifacts) | Read the [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/artifacts)**
# 💻 Run W&B Server Locally
W&B Server is a self-hosted Weights & Biases server. Securely and quickly deploy a W&B production server in Docker, Kubernetes, or in a privately-managed cloud. Learn more about setting up a [production W&B deployment →](https://docs.wandb.ai/guides/self-hosted/setup).
## Quickstart
1. On a machine with [Docker](https://docker.com) and [Python](https://www.python.org/) installed, run:
```
1 pip install wandb --upgrade
2 wandb server start
```
2. Generate a free license from the [Deployer](https://deploy.wandb.ai/).
3. Add it to your W&B Server's localhost's settings.
**Paste the license in the /system-admin page on your localhost**

## Docker
Running `wandb server start` will start our server and forward port 8080 on the host. To have other machines report metrics to this server run: `wandb login --host=http://X.X.X.X:8080`.
Use Docker to manually run W&B Local:
```
docker run --rm -d -v wandb:/vol -p 8080:8080 --name wandb-local wandb/local
```
# Testing
To run basic test use `make test`. More detailed information can be found at CONTRIBUTING.md.
We use [circleci](https://circleci.com) for CI.
# 📜 Share insights with Reports
Reports let you [organize visualizations, describe your findings, and share updates with collaborators](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o2dOSIDDr1w&&ab_channel=Weights%26Biases).
### Common use cases
- **Notes:** Add a graph with a quick note to yourself.
- **Collaboration:** Share findings with your colleagues.
- **Work log:** Track what you've tried and plan next steps.
**Explore reports in [The Gallery →](https://app.wandb.ai/gallery) | Read the [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/reports)**
Once you have experiments in W&B, you can visualize and document results in Reports with just a few clicks. Here's a quick [demo video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jWBGKGAjt6w&t=2s&ab_channel=Weights%26Biases).

# 🏺 Version control datasets and models with Artifacts
Git and GitHub make code version control easy,
but they're not optimized for tracking the other parts of the ML pipeline:
datasets, models, and other large binary files.
W&B's Artifacts are.
With just a few extra lines of code,
you can start tracking you and your team's outputs,
all directly linked to run.
### [Try Artifacts in a Colab →](http://wandb.me/artifacts-colab)

### Common use cases
- **Pipeline Management:** Track and visualize the inputs and outputs of your runs as a graph
- **Don't Repeat Yourself™:** Prevent the duplication of compute effort
- **Sharing Data in Teams:** Collaborate on models and datasets without all the headaches

**Learn about Artifacts [here →](https://www.wandb.com/articles/announcing-artifacts) | Read the [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/artifacts)**
# 💻 Run W&B Server Locally
W&B Server is a self-hosted Weights & Biases server. Securely and quickly deploy a W&B production server in Docker, Kubernetes, or in a privately-managed cloud. Learn more about setting up a [production W&B deployment →](https://docs.wandb.ai/guides/self-hosted/setup).
## Quickstart
1. On a machine with [Docker](https://docker.com) and [Python](https://www.python.org/) installed, run:
```
1 pip install wandb --upgrade
2 wandb server start
```
2. Generate a free license from the [Deployer](https://deploy.wandb.ai/).
3. Add it to your W&B Server's localhost's settings.
**Paste the license in the /system-admin page on your localhost**

## Docker
Running `wandb server start` will start our server and forward port 8080 on the host. To have other machines report metrics to this server run: `wandb login --host=http://X.X.X.X:8080`.
Use Docker to manually run W&B Local:
```
docker run --rm -d -v wandb:/vol -p 8080:8080 --name wandb-local wandb/local
```
# Testing
To run basic test use `make test`. More detailed information can be found at CONTRIBUTING.md.
We use [circleci](https://circleci.com) for CI. ### Common use cases
- **Explore:** Efficiently sample the space of hyperparameter combinations to discover promising regions and build an intuition about your model.
- **Optimize:** Use sweeps to find a set of hyperparameters with optimal performance.
- **K-fold cross validation:** [Here's a brief code example](https://github.com/wandb/examples/tree/master/examples/wandb-sweeps/sweeps-cross-validation) of _k_-fold cross validation with W&B Sweeps.
### Visualize Sweeps results
The hyperparameter importance plot surfaces which hyperparameters were the best predictors of, and highly correlated to desirable values for your metrics.
### Common use cases
- **Explore:** Efficiently sample the space of hyperparameter combinations to discover promising regions and build an intuition about your model.
- **Optimize:** Use sweeps to find a set of hyperparameters with optimal performance.
- **K-fold cross validation:** [Here's a brief code example](https://github.com/wandb/examples/tree/master/examples/wandb-sweeps/sweeps-cross-validation) of _k_-fold cross validation with W&B Sweeps.
### Visualize Sweeps results
The hyperparameter importance plot surfaces which hyperparameters were the best predictors of, and highly correlated to desirable values for your metrics.
 Parallel coordinates plots map hyperparameter values to model metrics. They're useful for honing in on combinations of hyperparameters that led to the best model performance.
Parallel coordinates plots map hyperparameter values to model metrics. They're useful for honing in on combinations of hyperparameters that led to the best model performance.
 # 📜 Share insights with Reports
Reports let you [organize visualizations, describe your findings, and share updates with collaborators](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o2dOSIDDr1w&&ab_channel=Weights%26Biases).
### Common use cases
- **Notes:** Add a graph with a quick note to yourself.
- **Collaboration:** Share findings with your colleagues.
- **Work log:** Track what you've tried and plan next steps.
**Explore reports in [The Gallery →](https://app.wandb.ai/gallery) | Read the [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/reports)**
Once you have experiments in W&B, you can visualize and document results in Reports with just a few clicks. Here's a quick [demo video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jWBGKGAjt6w&t=2s&ab_channel=Weights%26Biases).

# 🏺 Version control datasets and models with Artifacts
Git and GitHub make code version control easy,
but they're not optimized for tracking the other parts of the ML pipeline:
datasets, models, and other large binary files.
W&B's Artifacts are.
With just a few extra lines of code,
you can start tracking you and your team's outputs,
all directly linked to run.
### [Try Artifacts in a Colab →](http://wandb.me/artifacts-colab)

### Common use cases
- **Pipeline Management:** Track and visualize the inputs and outputs of your runs as a graph
- **Don't Repeat Yourself™:** Prevent the duplication of compute effort
- **Sharing Data in Teams:** Collaborate on models and datasets without all the headaches

**Learn about Artifacts [here →](https://www.wandb.com/articles/announcing-artifacts) | Read the [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/artifacts)**
# 💻 Run W&B Server Locally
W&B Server is a self-hosted Weights & Biases server. Securely and quickly deploy a W&B production server in Docker, Kubernetes, or in a privately-managed cloud. Learn more about setting up a [production W&B deployment →](https://docs.wandb.ai/guides/self-hosted/setup).
## Quickstart
1. On a machine with [Docker](https://docker.com) and [Python](https://www.python.org/) installed, run:
```
1 pip install wandb --upgrade
2 wandb server start
```
2. Generate a free license from the [Deployer](https://deploy.wandb.ai/).
3. Add it to your W&B Server's localhost's settings.
**Paste the license in the /system-admin page on your localhost**

## Docker
Running `wandb server start` will start our server and forward port 8080 on the host. To have other machines report metrics to this server run: `wandb login --host=http://X.X.X.X:8080`.
Use Docker to manually run W&B Local:
```
docker run --rm -d -v wandb:/vol -p 8080:8080 --name wandb-local wandb/local
```
# Testing
To run basic test use `make test`. More detailed information can be found at CONTRIBUTING.md.
We use [circleci](https://circleci.com) for CI.
# 📜 Share insights with Reports
Reports let you [organize visualizations, describe your findings, and share updates with collaborators](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o2dOSIDDr1w&&ab_channel=Weights%26Biases).
### Common use cases
- **Notes:** Add a graph with a quick note to yourself.
- **Collaboration:** Share findings with your colleagues.
- **Work log:** Track what you've tried and plan next steps.
**Explore reports in [The Gallery →](https://app.wandb.ai/gallery) | Read the [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/reports)**
Once you have experiments in W&B, you can visualize and document results in Reports with just a few clicks. Here's a quick [demo video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jWBGKGAjt6w&t=2s&ab_channel=Weights%26Biases).

# 🏺 Version control datasets and models with Artifacts
Git and GitHub make code version control easy,
but they're not optimized for tracking the other parts of the ML pipeline:
datasets, models, and other large binary files.
W&B's Artifacts are.
With just a few extra lines of code,
you can start tracking you and your team's outputs,
all directly linked to run.
### [Try Artifacts in a Colab →](http://wandb.me/artifacts-colab)

### Common use cases
- **Pipeline Management:** Track and visualize the inputs and outputs of your runs as a graph
- **Don't Repeat Yourself™:** Prevent the duplication of compute effort
- **Sharing Data in Teams:** Collaborate on models and datasets without all the headaches

**Learn about Artifacts [here →](https://www.wandb.com/articles/announcing-artifacts) | Read the [Docs](https://docs.wandb.com/artifacts)**
# 💻 Run W&B Server Locally
W&B Server is a self-hosted Weights & Biases server. Securely and quickly deploy a W&B production server in Docker, Kubernetes, or in a privately-managed cloud. Learn more about setting up a [production W&B deployment →](https://docs.wandb.ai/guides/self-hosted/setup).
## Quickstart
1. On a machine with [Docker](https://docker.com) and [Python](https://www.python.org/) installed, run:
```
1 pip install wandb --upgrade
2 wandb server start
```
2. Generate a free license from the [Deployer](https://deploy.wandb.ai/).
3. Add it to your W&B Server's localhost's settings.
**Paste the license in the /system-admin page on your localhost**

## Docker
Running `wandb server start` will start our server and forward port 8080 on the host. To have other machines report metrics to this server run: `wandb login --host=http://X.X.X.X:8080`.
Use Docker to manually run W&B Local:
```
docker run --rm -d -v wandb:/vol -p 8080:8080 --name wandb-local wandb/local
```
# Testing
To run basic test use `make test`. More detailed information can be found at CONTRIBUTING.md.
We use [circleci](https://circleci.com) for CI.